Human physiology
Human physiology is the study of the functions and processes that occur within the human body. It concerns the way in which our bodies work, and how they maintain homeostasis, or balance, to ensure that we remain healthy and functioning properly. The study of human physiology covers a wide range of disciplines, including anatomy, biochemistry, pharmacology, and neuroscience.
It involves the study of the various organs and systems that work together to maintain homeostasis, or balance, within the body.
Here are some of the major organs and systems of human physiology:
Nervous system: The nervous system is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves that extend throughout the body. It controls and coordinates the functions of the body and is responsible for processing information from the environment.
Endocrine system: The endocrine system is responsible for regulating the body’s hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by various glands in the body, such as the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pituitary gland. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to target cells, where they regulate various functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Cardiovascular system: The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. It includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the blood vessels transport the blood to various organs and tissues. The blood itself carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells, as well as waste products, such as carbon dioxide, away from the cells.
Respiratory system: The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It includes the lungs, trachea, and bronchi. The lungs are responsible for taking in oxygen, which is then transported to the cells by the cardiovascular system, and expelling carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of metabolism.
Digestive system: The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The process of digestion involves the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food, as well as the absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Urinary system: The urinary system is responsible for removing waste products from the body. It includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood, which are then excreted in the urine.
Muscular system: The muscular system is responsible for producing movement and maintaining posture. It includes skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.
Skeletal system: The skeletal system provides support for the body and protects internal organs. It includes bones, cartilage, and ligaments.
Integumentary system: The integumentary system is responsible for protecting the body from the environment. It includes the skin, hair, and nails.
Immune system: The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. It includes various cells and organs, such as the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. The immune system produces antibodies and other proteins that can identify and neutralize foreign invaders, helping to prevent infections and disease.
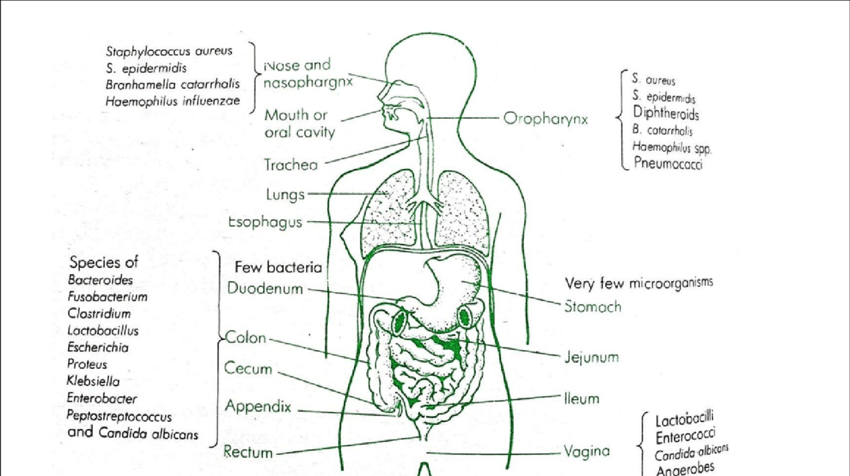
One of the most important functions of human physiology is the maintenance of homeostasis. This refers to the regulation of our internal environment to ensure that it remains within certain parameters, such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels. There are many different systems within the body that work together to maintain homeostasis, including the nervous system, endocrine system, and immune system.
The nervous system is responsible for controlling and coordinating the functions of the body. It is made up of the brain, spinal cord, and a network of nerves that extend throughout the body. The nervous system processes information from the environment, such as light or sound, and sends signals to the muscles and glands to respond accordingly. It also regulates internal processes, such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion.
The endocrine system is responsible for regulating the body’s hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by various glands in the body, such as the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pituitary gland. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to target cells, where they regulate various functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. It includes various cells and organs, such as the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. The immune system produces antibodies and other proteins that can identify and neutralize foreign invaders, helping to prevent infections and disease.
Another important aspect of human physiology is metabolism. This refers to the chemical reactions that occur within the body to break down food and convert it into energy. The process of metabolism is regulated by various hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, and is influenced by factors such as diet, exercise, and genetics.
The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. It includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the blood vessels transport the blood to various organs and tissues. The blood itself carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells, as well as waste products, such as carbon dioxide, away from the cells.
The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It includes the lungs, trachea, and bronchi. The lungs are responsible for taking in oxygen, which is then transported to the cells by the cardiovascular system, and expelling carbon dioxide, which is a waste product of metabolism.
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. The process of digestion involves the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food, as well as the absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Finally, the urinary system is responsible for removing waste products from the body. It includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste products from the blood, which are then excreted in the urine.
In conclusion, human physiology is a vital field of study that helps us understand the complex functions and processes that occur within the human body. It covers a wide range of disciplines and systems, all of which work together to maintain homeostasis and ensure that we remain healthy and functioning properly.


Pingback: Human Anatomy -
Pingback: Biochemistry -
Pingback: COMMUNITY MEDICINE -
Pingback: Fasting nutrition dietetics -
Pingback: The Role of Physiotherapy : Improving Physical Function and Enhancing Quality of Life -
Pingback: YOGA THERAPY: The Healing Power of Yoga -
Pingback: Acupressure - Healing power of acupressure -